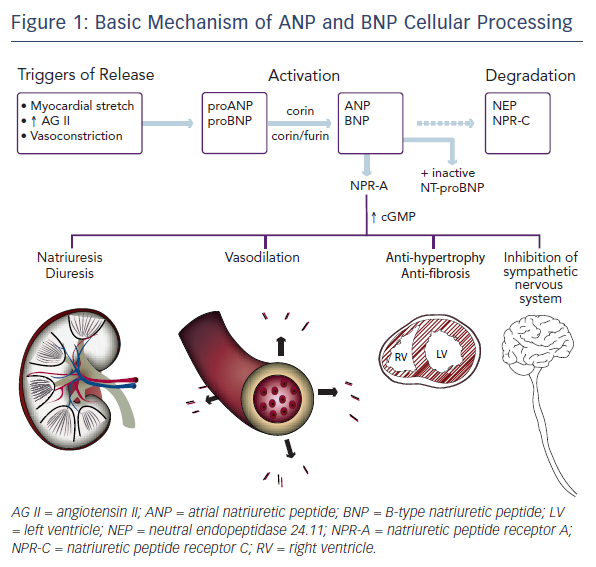
Today, natriuretic peptides are ubiquitously utilized for the diagnosis, treatment, and prognostication of heart failure in the Emergency Department, as well as inpatient and outpatient settings alike.1–5 These endogenous hormones counteract some of the most detrimental effects of heart failure. Given their clinical and physiological importance, the fact that a manuscript describing the vasodilatory, diuretic, and natriuretic properties of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) – the first natriuretic peptide to be identified – was initially rejected from publication in 1980 today seems astonishing.6 The discovery propelled subsequent investigation that still continues over 30 years later. Much more detail is now known about these chemical messengers. This article reviews the current understanding of the compensatory actions of cardiac natriuretic peptides in heart failure and how this knowledge is revolutionizing heart failure therapy.
Background
Structurally related and made biologically active by a 17-amino-acid core ring and a cysteine bridge,7 the natriuretic peptides are a group of compounds that possess diverse actions in cardiovascular, renal, and endocrine homeostasis. The most recognized are ANP and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), which are released from both the atria and ventricles,8,9 and are the focus of this review. Other known natriuretic peptides include C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), which is derived in the endothelium,10 Dendroaspis natriuretic peptidelike immunoreactivity (DNP-LI), which is present in the normal atrial myocardium and named for its structural similarity to a natriuretic peptide found in Dendroaspis angusticeps snake venom,11 and urodilatin, which is a component of human urine.12
Both ANP and BNP are secreted as pre-pro-polypeptides – that is, they are produced as inactive proteins attached to an N-terminal signal peptide, which is removed in the endoplasmic reticulum. After removal of the signal peptide, proANP – a 126-amino acid peptide – is stored in cardiac atria granulae.8 Upon cellular stimulation, such as myocardial stretch, vasoconstriction by endothelin, or increased levels of angiotensin II, a serine protease called corin cleaves proANP into the 28-amino-acid active ANP. In a normal healthy heart, ANP is not found in the ventricles. Heart failure is associated with a decrease in atrial ANP and increase in ventricular myocyte ANP.13
The mechanism of BNP activation is similar. Its pre-pro-polypeptide contains 134-amino acids.8 Removal of the N-terminal signal peptide generates proBNP1-108, which, after cellular stimulation, is cleaved by the serine proteases furin and corin into inactive N-terminal-proBNP (NT-proBNP) and active BNP1-32.14–16 Paralleling the expression of ANP in the progression of heart failure, the expression of BNP is solely derived from the atria in normal healthy conditions, increasing in the atria in early left ventricular dysfunction, and only later rising in the ventricle in overt volume overload.9
Active ANP and BNP bind to their receptor, natriuretic peptide receptor A (NPR-A), which is widely expressed in the body, including in the kidney, heart, lungs, brain, adrenal glands, adipose tissue, and vasculature. This binding activates guanylyl cyclase. The resulting increase in cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) mediates several protective mechanisms within the renal, vascular, and cardiac systems as discussed below. The active peptides are removed from circulation by natriuretic peptide receptor C (NPR-C) and degraded by neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (NEP), also known as neprilysin.8,17 Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is also involved in natriuretic peptide cleavage.18Figure 1 shows a simplified portrait of ANP and BNP cellular processing.
Physiological Effects
The neurohumoral response to heart failure is complex and incompletely understood. It involves a multitude of peptides and mediators. One can consider a simplified model composed of two opposite yet complementary forces, though. On one hand are the sympathetic nervous system, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, and vasopressin, which work together to preserve cardiac output via fluid retention, augmented contractility, and increased heart rate. These effects are vasoconstricting, anti-natriuretic, anti-diuretic, and growth-promoting. On the other hand are the natriuretic peptides, which are vasodilating, natriuretic, diuretic, and anti-mitogenic, protecting against fibrosis and hypertrophy.19–25 BNP may inhibit the sympathetic nervous system directly as well.26
At first, the two sides seem to function in harmony. But chronically, the continuous fight to maintain cardiac output leads to volume overload. Natriuretic peptides eventually fail to compensate, and a vicious cycle of worsening heart failure perpetuates itself.
What causes the collapse of these compensatory measures? The breakdown is multifactorial. Studies suggest that in acute heart failure, the body reaches a maximum level of circulating natriuretic peptide that cannot be surpassed with greater elevations in atrial pressure.27,28 Even as higher pressures become longstanding, the body still cannot mount more natriuretic peptide, underscoring an impaired compensatory capacity during chronic volume overload.27 Research has also demonstrated reduced corin levels and predominantly altered, inactive forms of natriuretic peptide in patients with decompensated heart failure.29,30 High-molecular-weight forms of BNP, for example, have been isolated from patient samples, likely a combination of proBNP1-108 and its polymers.31–35 Further proteolyzed, degraded forms of BNP have also been quantified.36
Inability to produce and release active forms of natriuretic peptide is not the only hindrance to the body’s efforts to protect itself. In chronic severe heart failure, the end organs are also unable to respond fully to the hormone that is released into the bloodstream. Blunted natriuresis and vasodilatation have been shown in experimental heart failure.37–39 Explanations for the attenuated response to natriuretic peptides in chronic heart failure include NPR-A downregulation and desensitization to cGMP due to chronically high ANP and BNP levels. Tsutamoto et al. compared the plasma ANP and cGMP levels in patients with chronic mild to moderate heart failure with those in patients with chronic severe heart failure.40 Although plasma ANP and cGMP levels were positively correlated in the first group, no significant correlation was found in the latter group.40 Moreover, despite high concentrations of ANP in patients with chronic severe heart failure, cGMP concentrations plateaued.40
Therapeutic Strategies
Given the beneficial effects of natriuretic peptides, four main strategies seem plausible for increasing their plasma concentrations in hopes of potentiating and prolonging their compensatory actions: 1) by activating corin and furin; 2) by administering recombinant natriuretic peptides; 3) by antagonizing NPR-C; or 4) by inhibiting NEP. Of these targets, recombinant natriuretic peptides and NEP inhibitors have been most actively developed and hold the most clinical promise.
Recombinant Natriuretic Peptides
Infusions of synthetic ANP (such as anaritide and carperitide) have been used for years in Japan to treat hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure.41 Small s udies of synthetic ANP in chronic heart failure as well have demonstrated vasodilatory and diuretic benefits, in addition to enhanced renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate.42,43 Synthetic BNP (nesiritide), however, has made bigger headlines in the US since it gained US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 2001.
Colucci et al. first studied the clinical use of nesiritide in hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure in a two-part multi-center study: an efficacy trial and a comparative trial.44 The efficacy trial, which aimed to evaluate the drug’s short-term effects on haemodynamics, global clinical status (judged independently by both the patient and the investigator), and symptoms, included 127 patients with a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) of at least 18 mmHg and a cardiac index of no more than 2.7 l/min/m2. Using a double-blind placebo-controlled design, the subjects were randomised to a 6-hour infusion of either placebo or low- or high-dose nesiritide. The low-dose group received a 0.3 μg/kg bolus followed by an infusion at 0.015 μg/kg/min. The high-dose group received a 0.6 μg/kg bolus followed by 0.030 μg/kg/min.
Results demonstrated a dose-dependent and statistically significant decrease in PCWP and increase in cardiac index in the nesiritide groups (p<0.001). Patient-reported global clinical status improvement was noted in 60 % and 67 % of patients in the low- and high-dose nesiritide groups, respectively, compared with 14 % of patients receiving placebo (p<0.001 for both comparisons). Physician-reported global clinical status improvement was observed in 55 % and 77 % of patients in the low- and high-dose nesiritide groups, respectively, compared with 5 % of patients receiving placebo (p<0.001 for both comparisons). Similarly, patients on nesiritide reported statistically significant improvements in dyspnea and fatigue.
In the comparative trial, 305 patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to ‘open label standard therapy’ (consisting of single vasoactive drug therapy, such as dobutamine, milrinone, nitroglycerin, or nitroprusside) or double-blind dosing of nesiritide (at the same dosing as the efficacy trial) for up to 7 days. Most patients in the study were treated for 1–2 days, and all groups witnessed improvement in global clinical status, dyspnea, and fatigue at 6 hours, 24 hours, and at the end of therapy. None of the results showed significant differences between nesiritide and standard therapy, though.
Dose-related hypotension was the main adverse effect in these trials. Although predominantly asymptomatic, symptomatic hypotension occurred in 4 % of the standard-therapy group in the comparative trial, compared with 11 % and 17 % of the low- and high-dose nesiritide groups, respectively (p=0.008). The investigators argued that in clinical practice, the incidence of hypotension would be minor because the initial nesiritide dose would be low and titrated to blood pressure. Overall, the study concluded that nesiritide could achieve rapid symptomatic relief and improved haemodynamics in hospitalized patients.44
Given questions over adverse blood pressure effects, a larger bolus dose but smaller infusion dose was used in the Vasodilatation in the Management of Acute Congestive Heart Failure (VMAC) trial.45 This multi-center prospective, randomised, double-blind trial sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravenous nesiritide compared with intravenous nitroglycerin and placebo. The study involved 489 hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure and New York Heart Association class IV symptoms. Nesiritide was given as a 2 μg/kg bolus followed by an infusion of 0.01 μg/kg/min for 3 hours. At 3 hours, reduction in PCWP from baseline was significantly greater in the nesiritide group (p<0.001 compared with placebo; p=0.03 compared with nitroglycerin). Although nesiritide provided significant symptomatic relief compared with the placebo, no significant difference was found compared with nitroglycerin. Rates of hypotension were similar between nesiritide and nitroglycerin, and again, most hypotensive episodes were mild.45
Skepticism over the drug continued when a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials later raised concern that nesiritide significantly increased the risk of renal impairment, even at the lowest dose.46 In response to the enormous controversy, the Acute Study of Clinical Effectiveness of Nesiritide in Decompensated Heart Failure (ASCEND-HF) was undertaken. The trial randomised 7,141 patients with acute, decompensated heart failure to receive standard therapy in addition to either placebo or nesiritide.47 ASCEND-HF confirmed that nesiritide had no effect on renal function. Investigators postulated that the meta-analysis results were at least in part due to inclusion of studies that did not compare nesiritide with a placebo but with drugs like dobutamine or nitroglycerin, which could have improved renal function. Still, the earlier concerns, coupled with studies highlighting lack of significant improvement in re-hospitalisation, mortality, or symptoms, led to a drastic decrease in the use of nesiritde.48,49
NEP Inhibition
After the rise and fall of synthetic BNP, investigators have focused more on NEP inhibition. Small studies with NEP inhibitors like candoxatril and sinorphan have shown that halving NEP activity effectively doubles the ANP level.50 NEP inhibition also circumvents the unwanted physiological effects of diuretic therapy like increased renin and aldosterone.51 Some studies reported clinical benefits, although the results were limited by very short-term therapy. One of them found an association with decreased PCWP, but only 12 male patients were included, with a treatment duration of 2 days.50 Another study demonstrated improved exercise duration over 12 weeks of therapy, although the result was not statistically significant.52 Despite these promising characteristics, NEP inhibitors did not result in a significant decrease in blood pressure;53 in fact, these drugs actually increased systolic pressure in healthy subjects.54 This initially unexpected effect was later attributed to the fact that angiotensin II and endothelin I are NEP substrates as well.55,56 As such, the haemodynamic result of NEP inhibitors is not simply a vasodilatory response to increased natriuretic peptide levels but dependent on the net balance with its vasopressor effects as well.
The complex interaction between these drugs and the renin– angiotensin–aldosterone system was demonstrated in a study in which two groups of healthy subjects displayed opposite haemodynamic responses to NEP inhibition.57 Subjects were pretreated with either low or high doses of candoxatril, then administered stepwise infusions of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II concentrations were augmented in both groups, particularly with higher doses of candoxatril. Whereas the lower dose of candoxatril was associated with about a 10 mmHg increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressures, the higher dose was not.57 Possible explanations were that the modest negative sodium balance that resulted in the high-dose group reduced the pressor response to angiotensin II, and that higher doses of candoxatril enhanced ANP enough to offset the angiotensin II pressor action as well. These results suggested that in high renin states, NEP inhibitors could exacerbate hypertension; but in low renin states, these drugs could potentiate vasodilation.
Combination Therapy
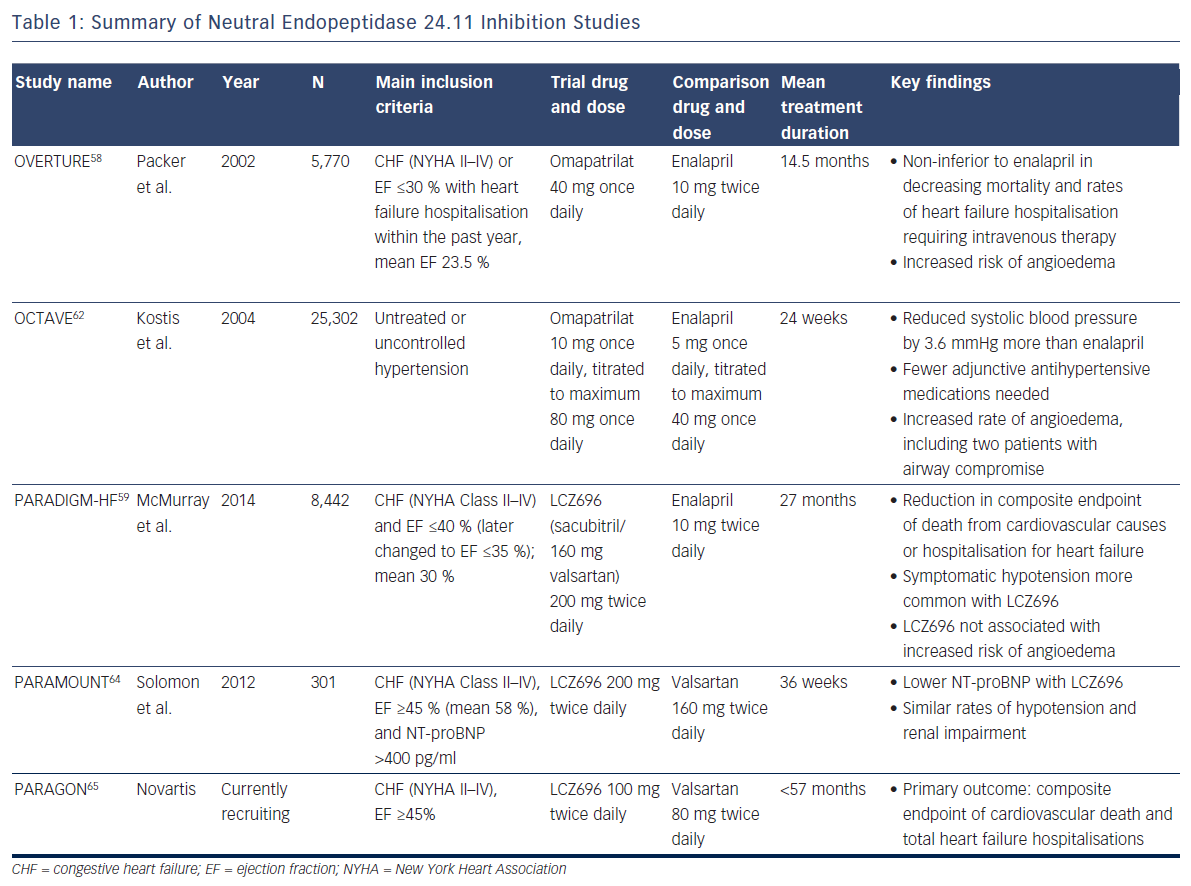
To combat the blood pressure effect, ‘vasopeptidase inhibitors’ like omapatrilat – containing a combination of an angiotensin-convertingenzyme (ACE) inhibitor and a NEP inhibitor – were developed. But, despite its theoretical promise, omapatrilat had disappointing results. In the Omapatrilat versus Enalapril Randomised Trial of Utility in Reducing Events (OVERTURE), the study drug proved non-inferior to enalapril in decreasing mortality and rates of heart failure hospitalisation requiring intravenous therapy among 5,770 patients, but more patients treated with omapatrilat experienced angioedema (0.8 % versus 0.5 % with enalapril)58, likely because bradykinin is also a substrate of NEP.59 More specifically, bradykinin degradation is dependent on ACE, aminopeptidase P, dipetidyl peptidase IV, and NEP.60 Many ACE inhibitors are known to inhibit aminopeptidase P as well.61 In the face of a NEP inhibitor/ACE inhibitor combination drug, bradykinin clearance relies heavily on dipetidyl peptidase IV, whereas an ACE inhibitor alone produces less blockade of these metabolic pathways (as does a combination NEP inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker).
The Omapatrilat Cardiovascular Treatment Assessment Versus Enalapril (OCTAVE) study employed lower doses of omapatrilat in 25,302 patients with hypertension (not heart failure) and again confirmed significantly more cases of angioedema (2.2 versus 0.7 %; p<0.005).62 Given the lack of benefit in heart failure compared with standard therapy, and significant safety concerns, the drug never gained FDA approval.
Researchers returned to the drawing boards, formulating a plan to combat the unwanted angioedema of omapatrilat while still considering the lessons learned from prior manipulations of the natriuretic peptide system. The result was LCZ696: a combination of the angiotensin II receptor blocker valsartan and NEP inhibitor sacubitril. So far, the drug has achieved very promising results.
The Prospective comparison of Angiotensin Receptor neprilysin inhibitors with Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGMHF) study was stopped early due to the unequivocal benefit found with LCZ696 after a median follow-up of 27 months.59,63 This double-blind study of 8,442 patients with symptomatic chronic systolic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction of ≤40 % (the protocol was later adjusted to ≤35 %, and the mean was 30 %) compared twice daily dosing of LCZ696 with enalapril, showing reduction in the composite endpoint of death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalisation for heart failure (hazard ratio 0.80; 95 % CI [0.73–0.87]; p<0.001), as well as a reduction in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio 0.84; 95 % CI [0.76–0.93]; p<0.001).59 Symptomatic hypotension was more common with LCZ696 than with enalapril but did not lead to increased discontinuation of therapy. Two welcomed results with respect to the previous nesiritide and omapatrilat controversies were: 1) increases in serum creatinine and related discontinuation of therapy were more common with enalapril; and 2) as expected, LCZ696 was not associated with an increased risk of angioedema59 (since this drug leaves both ACE and aminopeptidase P to clear bradykinin). Criticisms of PARADIGM-HF include that although LCZ696 employs the maximum dose of valsartan, the study compared the drug with half the maximum dose of enalapril.
With these promising findings, investigators sought to determine whether substantial morbidity and mortality benefit extended to heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction. The first step was the Prospective Comparison of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor with angiotensin receptor blocker on Management of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (PARAMOUNT) study, a phase-2, randomised, double-blind trial to examine the efficacy and safety of LCZ696 in this population. Patients were randomised to 200 mg of LCZ696 twice daily or 160 mg valsartan twice daily for 36 weeks. Chosen for its association with adverse outcomes in heart failure patients, the primary endpoint examined change in NT-proBNP. Results demonstrated a greater reduction in NT-proBNP in the LCZ696 group (p=0.01), and similar rates of hypotension and renal impairment compared with valsartan alone.64 The Prospective comparison of Angiotensin Receptorneprilysin inhibitor with Angiotensin receptor blocker Global Outcomes in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (PARAGON) trial is a phase-3 study aiming to build on this data and support the morbidity and mortality benefit seen in PARADIGM-HF for heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction.65
The NEP inhibition studies are summarized in Table 1.
Effect of NEP Inhibition on Clinical use of Natriuretic Peptide Levels
Current American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF)/American Heart Association (AHA) heart failure practice guidelines give measurement of BNP or NT-proBNP a Class I recommendation for both diagnosing and establishing prognosis in heart failure, and a Class II recommendation for guiding therapy.66 With the FDA approval of LCZ696 (sacubitril/valsartan), important questions arise as to how this drug and other neprilysin inhibitors will affect the clinical interpretation of natriuretic peptide levels for each of these indications. In the PARADIGMHF trial, LCZ696 was associated with a significant increase in BNP and urinary cGMP levels at 4 weeks and 8 months compared with enalapril (p<0.0001).67 In contrast, NT-proBNP and troponin T levels were lower in patients receiving LCZ696 than in those receiving enalapril (p<0.0001). A similar effect on NT-proBNP levels was seen in PARAMOUNT.64
The PARADIGM-HF authors suggest that among patients receiving LCZ696, increased levels of BNP may be related to the mechanism of the drug (since inhibiting neprilysin augments BNP concentration), whereas decreased levels of NT-proBNP (which is not a substrate for neprilysin) may be indicative of the cardiac effects of the drug in reducing wall stress and myocyte injury.67 If this hypothesis is correct, NT-proBNP may be a more appropriate marker choice for monitoring heart failure patients on neprilysin inhibitors, though this theory has not yet been proven. If true, ANP, CNP, and their respective N-terminal peptides could also be considered as monitoring biomarkers, as neprilysin has higher affinity for these peptides;68 assays for NT-proBNP and BNP, however, are currently in wider clinical use.
An alternate explanation is possible. Analyses of blood samples from heart failure patients reveal that proBNP and NT-proBNP undergo post-translational modifications including glycosylation at several sites.69 Most assays for NT-proBNP rely on antibodies directed against epitopes that can undergo glycosylation.69,70 Glycosylation, however, interferes with antibody binding.69 Neprilysin inhibitors may cause assays to underrepresent the actual concentration of NT-proBNP by increasing glycosylation of NT-proBNP.71 How these neprilysin inhibitor-induced changes in natriuretic peptide measurements will affect the accuracy and implications of assay results has not been studied yet. At the very least, cutpoints will likely need to be recalibrated for use in patients on these drugs, particularly if BNP is being measured. Regardless, more studies are needed to help guide the optimal use of BNP and/or NT-proBNP measurements in patients taking neprilysin inhibitors.
Conclusion
Great steps have been made in harnessesing the understanding of natriuretic peptide processing and signaling for heart failure therapy. The resulting drugs have aimed to reinforce the ability of natriuretic peptides to compensate for the ill-effects of the sympathetic nervous system and renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in chronic heart failure. Despite the latest success in NEP inhibitor combination therapies, controversy surrounding these drugs has not waned, including a theoretical concern of reduced amyloid beta degradation and consequent increased longterm risk of Alzheimer’s dementia.72 Clinicians still must weigh the intended benefits with the potential unwanted side effects of these therapies. The long-term efficacy and risks of these drugs are still unknown, as are the optimal ways to utilise natriuretic peptide assays in patients on these drugs, and their economic impacts, though much of these uncertainties will be sorted out with time. So far, this story is one of success, but its ending remains unwritten as we await further data to guide our targeted titration of agents in the natriuretic peptide system to the benefit of our patients.