Nearly half of patients with heart failure (HF) in the community have HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and mortality and morbidity in this group of patients is high.1–4 However, to date, there is no established pharmacotherapy to improve survival in HFpEF.5–9 Patients with HFpEF are often elderly and their primary chronic symptom is severe exercise intolerance, which results in a reduced quality of life.10,11 There is much evidence that left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is associated with the pathophysiology of HFpEF and that LV diastolic dysfunction contributes importantly to exercise intolerance in HFpEF patients.12–18 Furthermore, emerging evidence suggests that non-cardiac factors such as skeletal myopathy and vascular dysfunction also contribute to exercise intolerance in this patient group.4,19–21
The effect of exercise training on LV diastolic function in HFpEF has been examined in many randomised clinical trials (RCTs). The aim of this brief review is to summarise the RCTs examining the effects of exercise training on LV structure and function, as well as exercise capacity in HFpEF patients.
Pathophysiology of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
HF is defined as the pathological state in which the heart is unable to pump blood at a rate required by the metabolising tissues or can do so only with an elevated filling pressure. Inability of the heart to pump blood sufficiently to meet the needs of the body’s tissues may be due to the inability of the LV to fill (diastolic performance) and/or eject (systolic performance). When the HF is associated with a reduced ejection fraction (EF), the pathological state is called HF with reduced EF (HFrEF). In contrast, when the heart failure occurs in the absence of a reduced EF, the pathological state is called HFpEF.22 HFrEF and HFpEF have several similarities in LV structural and functional characteristics, including increased LV mass and increased LV end-diastolic pressure. The clearest difference between the two forms of HF is the difference in LV geometry and LV function; HFrEF is characterised by LV dilatation, eccentric LV hypertrophy and abnormal systolic and diastolic function, whereas HFpEF is characterised by concentric LV hypertrophy, a normal or near-normal EF and abnormal diastolic function.23 Exercise capacity is similarly impaired in HFrEF and HFpEF.24
Limited exercise tolerance because of fatigue and dyspnoea is a major symptom and a cause of disability in HFpEF. It results from abnormal central haemodynamics and peripheral non-cardiac factors. Abnormal central haemodynamics includes the inability to maintain (or augment) LV stroke volume adequately or maintaining (or augmenting) LV stroke volume at the expense of exaggerated increase in LV filling pressure during exercise.25 In addition, limited increase in HR during exercise (chronotropic incompetence) also contributes to limited increase in cardiac output. Peripheral non-cardiac factors contributing to exercise intolerance include impaired vascular function and alterations in the skeletal muscle. In HFpEF patients, arterial stiffness is increased and endothelial function is impaired, both of which contribute to the exercise intolerance.19 Furthermore, recent studies have shown that alterations in skeletal muscle, such as impaired microvascular function, reduced capillary density and mitochondrial dysfunction, are important contributors to exercise intolerance in HFpEF patients.4,20,21
Effect of Exercise Training in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
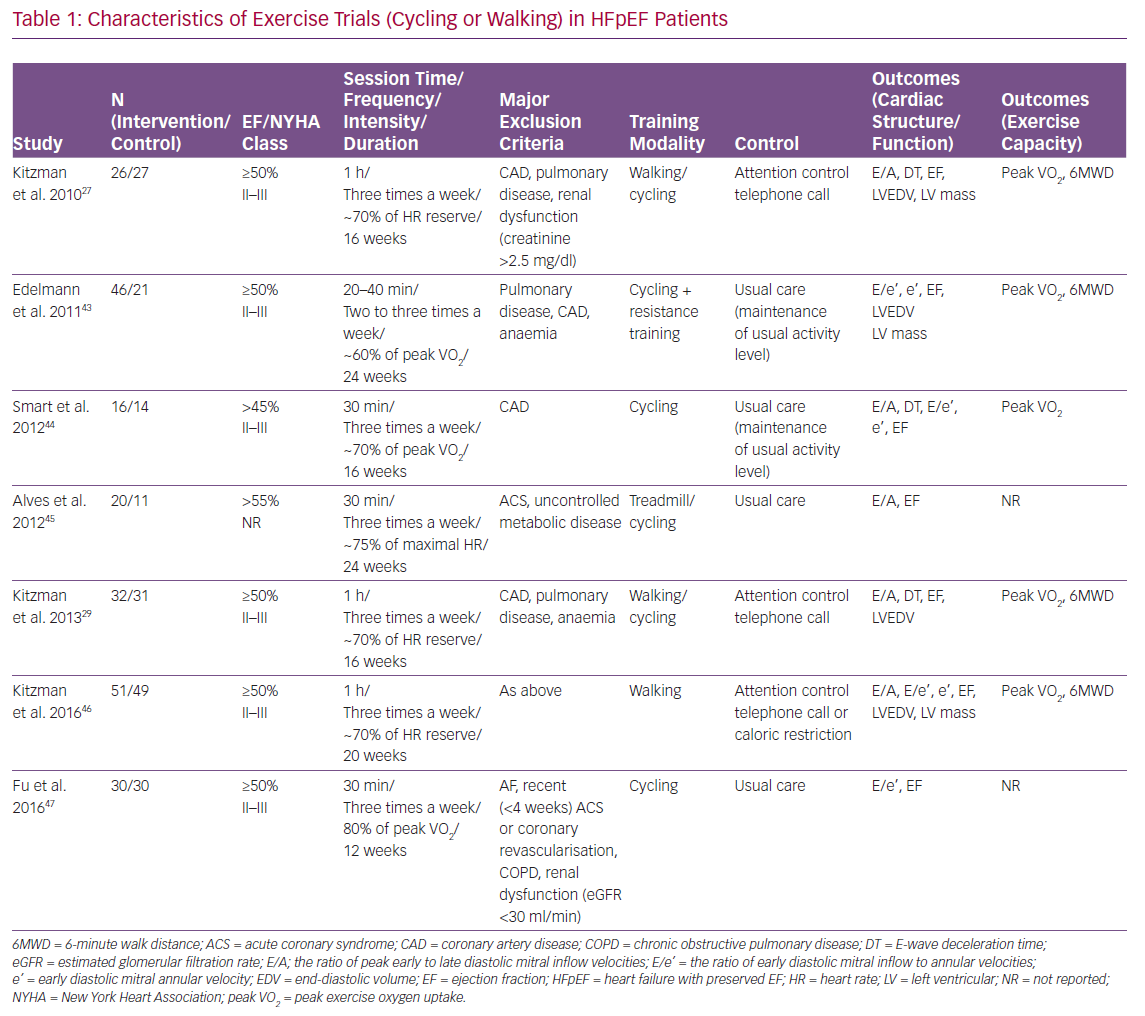
Many RCTs have reported the effect of exercise training on LV structure and function, as well as exercise capacity in HFpEF. Most of these trials used cycling and/or walking as the primary training modality (Table 1). Other physical training modalities included inspiratory muscle training and functional electrical stimulation of the lower limbs (Tables 2 and 3). Of note, most of the participants in these RCTs were taking standard medications for HF, such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers and diuretics.
Cycling or Walking
The effect of cycling or walking on LV structure and function, as well as exercise capacity in HFpEF, has been examined in seven RCTs (Table 1). A meta-analysis of these RCTs has recently been reported.26 In the meta-analysis, the ratio of peak early to late diastolic mitral inflow velocities (E/A), E-wave deceleration time, ratio of early diastolic mitral inflow to annular velocities (E/e), and early diastolic mitral annular velocity (e’) were extracted for the measures of LV diastolic function; peak exercise oxygen uptake (VO2) by expired gas analysis and 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) for the measures of exercise capacity; LV end-diastolic volume and LV mass for the measures of LV structure; and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) for the measure of LV systolic function. HR reserve, which was defined as the difference between peak HR during exercise test and HR before exercise, was also extracted.
In the pooled analyses, cycling and/or walking did not significantly change LV diastolic function in HFpEF patients. There was no significant difference in changes of E/A (weighted mean difference [WMD] 0.030; 95% CI [−0.023–0.082]; I2=6.252%; p=0.266), E-wave deceleration time (WMD −2.040; 95% CI [−26.534–22.454] ms; I2=50%; p=0.870), or e’ (WMD 0.317; 95% CI [−0.952–1.587] cm/s; I2=87.523%; p=0.624) between exercise training and control groups. Similarly, the exercise training did not significantly change LV structure and systolic function. There was no significant difference in changes of LV end-diastolic volume (standardised mean difference [SMD] −0.034; 95% CI [−0.276–0.208]; I2=0%; p=0.784), LV mass (SMD 0.072; 95% CI [−0.205–0.350]; I2=0%; p=0.609) or LVEF (WMD 0.850; 95% CI [−0.128–1.828]; I2=0%; p=0.088) between the exercise training and control groups.
Despite the neutral effect on LV structure and function, cycling and/or walking improved exercise capacity in HFpEF patients. Exercise training significantly increased peak VO2 (WMD 1.660; 95% CI [0.973–2.348] ml/min/kg; I2=21%; p<0.001) and 6MWD (WMD 33.883; 95% CI [12.384–55.381] m; I2=0%; p<0.01) compared with the control group. Furthermore, exercise training increased HR reserve compared with the control group (WMD 7.521; 95% CI [1.797–13.246] bpm; I2=0%; p<0.05).
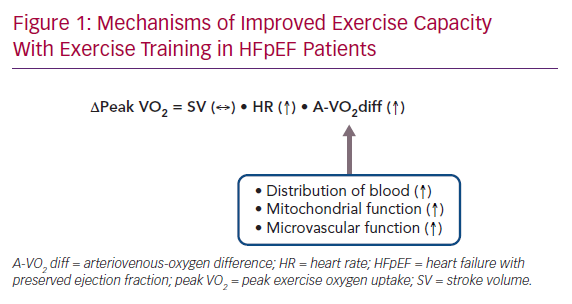
The meta-analysis clearly showed that exercise training improved exercise capacity without an improvement in LV structure or function in HFpEF patients.26 To consider the possible mechanisms for these observations, it may be useful to look over the pathophysiological background of exercise intolerance in HFpEF patients. During exercise, oxygen consumption in the metabolising tissues increases dramatically. Normally, this is accomplished by an increase in cardiac output (a product of HR and stroke volume) and an increased use of oxygen by the metabolising tissues. Earlier studies have reported that, in HFpEF patients, stroke volume during exercise increases or is maintained at the expense of increased LV end-diastolic pressure due to diastolic abnormalities, resulting in exertional dyspnoea.15–18 However, emerging data suggest that chronotropic incompetence, as well as peripheral non-cardiac factors, such as reduced oxygen delivery to exercising skeletal muscle and impaired oxygen use by active muscles during exercise, may play a relatively greater role in limiting exercise performance in HFpEF patients.4,20,21
Considering these points, the following mechanisms may underlie the improved exercise capacity with exercise training in HFpEF patients. In pooled analyses, exercise training improved HR reserve but not LV diastolic or systolic function.26 Thus, improved chronotropic incompetence resulting from exercise training may contribute at least in part to improved exercise capacity in HFpEF patients. Furthermore, in an ancillary study of the included trial, exercise training increased use of oxygen by active muscles but not peak stroke volume during exercise.27,28 Finally, another included trial reported that exercise training did not improve endothelial function or arterial stiffness, both of which are important determinants of exercise intolerance in HFpEF patients.29 Taken together, in HFpEF patients, the improved exercise capacity with exercise training may result from improved chronotropic incompetence, as well as increased use of oxygen by active muscles (Figure 1).
Although the mechanisms underlying increased use of oxygen by active muscles with exercise training remain elusive, several potential mechanisms have been proposed. First, improvement in skeletal muscle mitochondrial function with exercise training may be a significant contributor to increased use of oxygen in HFpEF patients. Multiple reports support that muscle mitochondrial function is impaired in HFpEF and is a strong factor for reduced use of oxygen.4,20,21 In an animal model of HFpEF, exercise training prevented the impairment of mitochondrial function.30 Second, exercise-induced upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthetase may increase bioavailability of nitric oxide, thereby improving vascular function and increasing distribution of blood to skeletal muscle.31 Finally, exercise training may induce anti-inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing metabolic inflammation and oxidative stress and improving microvascular circulation in skeletal muscle.31
The neutral effect of exercise training on LV structure and function should be interpreted with caution. First, exercise intervention period was relatively short (12–24 weeks; Table 1). Further studies are necessary to examine whether longer exercise intervention may favourably affect LV structure and function in HFpEF patients. Second, Doppler measurements of LV diastolic function at rest may be insufficient to detect subtle changes in diastolic function with exercise training. Because more sophisticated measurements of diastolic function, such as left atrial strain, have been developed, the effect of exercise training on the newly developed measurements merits further investigation. Finally, many HFpEF patients experience dyspnoea only during exertion. In these patients, LV filling pressure becomes markedly elevated during exercise. However, no included trials examined the effect of exercise training on LV function or LV filling pressure during exercise. Future trials should examine the effect of exercise training on LV function measures during exercise using exercise echocardiography.
Although minimal clinically important differences in exercise capacity in HFpEF patients have not been established, the reported improvements of 1.660 ml/min/kg in peak VO2 and 33.883 m in 6MWD with exercise training in the meta-analysis26 appear to be clinically important based on the results of earlier studies. Specifically, a mean change of 15.9–55.2 m in 6MWD has been reported to be associated with a mild to moderate improvement in HF status in HFrEF patients.32 Additionally, a meta-analysis of 22 RCTs with 3,826 HFrEF patients showed improvements of 1.85 ml/min/kg in peak VO2 and 47.9 m in 6MWD with exercise training.33 Finally, even small increments in peak VO2 following exercise training have been reported to be associated with improved survival in patients with a wide range of cardiovascular diseases and healthy subjects.34
Recent studies have shown that up to one-third of patients fail to demonstrate a meaningful increase in peak VO2 in response to exercise training, despite adequate compliance to training.34 Factors possibly influencing the response to exercise training are varied and are grouped as cardiac (systolic and diastolic function, chronotropic incompetence), non-cardiac (skeletal myopathy, vascular function, endothelial function, autonomic control), external (adherence, exercise dose and intensity) and comorbidities (obesity, anaemia, kidney diseases and pulmonary diseases). However, which factors predict the response to the training remains to be elucidated and warrants future investigation.
Inspiratory Muscle Training
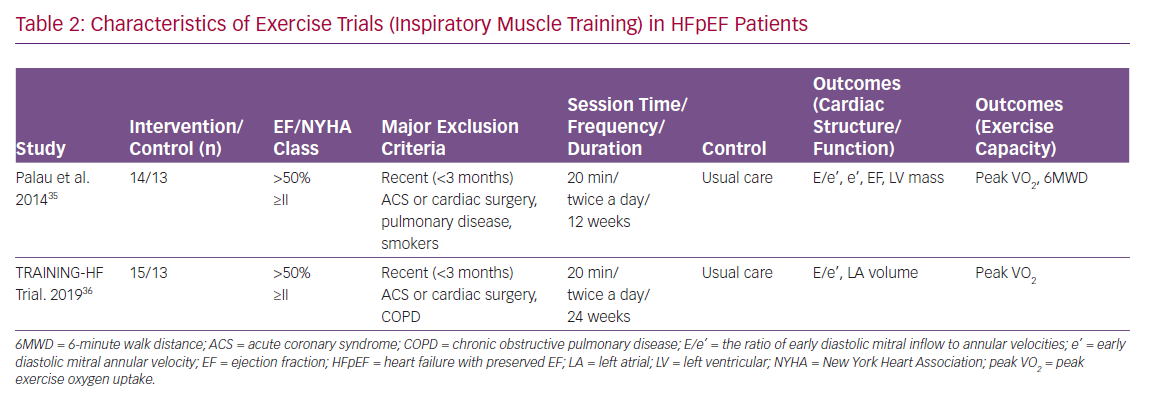
The effect of inspiratory muscle training on LV structure and function, as well as exercise capacity in HFpEF, has been examined in two RCTs (Table 2).35,36 Specifically, Palau et al. reported that 12-week inspiratory muscle training did not significantly change LV diastolic function; there was no significant difference in changes of e’ or E/e’ between the training and control groups. Similarly, the training did not significantly change LV systolic function or LV structure; there was no significant difference in changes of LVEF or LV mass between the training and control groups.
Despite the neutral effect on LV structure or function, inspiratory muscle training significantly increased peak VO2 (3.9 ml/min/kg; p<0.001) and 6MWD (67.4 m; p<0.001) compared with control group. Furthermore, the training reduced resting HR (−6 BPM; p<0.05) and increased peak exercise HR (5 BPM; p<0.01) compared with the control group, indicating that the training improved HR reserve.
Similar results have been reported recently by the same investigators.36 In the Inspiratory Muscle Training and Functional Electrical Stimulation for Treatment of HFpEF (TRAINING-HF) trial, 12-week inspiratory muscle training did not change cardiac function or structure; there was no significant difference in changes of E/e’ or left atrial volume index between exercise training and control groups. Despite the neutral effect on cardiac structure or function, inspiratory muscle training improved peak VO2 (2.98 ml/min/kg; p<0.001) compared with the control group.
Patients with congestive HF reportedly have reduced maximal inspiratory pressure and endurance of inspiratory muscle, both of which contribute to the exercise intolerance.37 Inspiratory muscle training may delay the development of diaphragmatic fatigue and increase ventilatory efficiency, resulting in an improvement in exercise capacity in HF patients.38
The reported improvement in peak VO2 with inspiratory muscle training is greater compared to that with cycling or walking.35,36 However, there are no RCTs comparing the effect of inspiratory muscle training versus cycling or walking on exercise capacity in HFpEF patients. The comparative effectiveness of inspiratory muscle training and cycling or walking in HFpEF patients merits further investigation.
Functional Electrical Stimulation
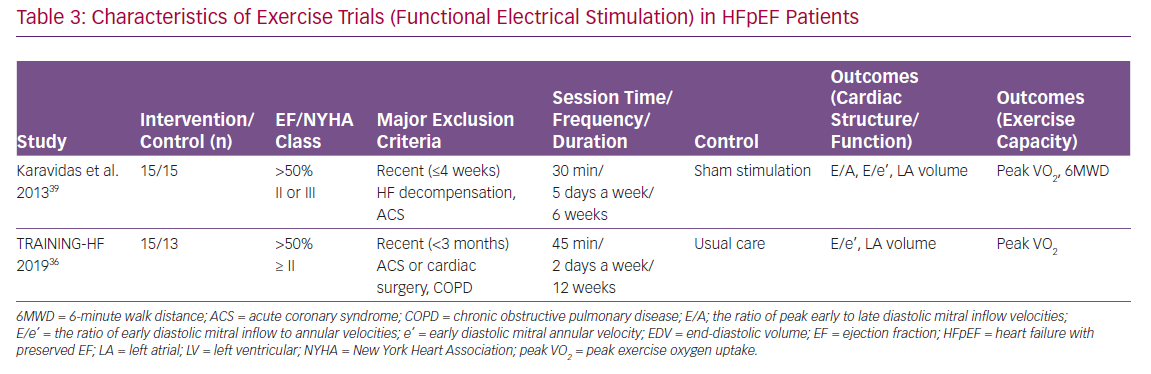
The effect of functional electrical stimulation of the lower limbs on cardiac structure and function as well as exercise capacity in HFpEF has been examined in two RCTs (Table 3).36,39 Specifically, Karavidas et al. reported that 6-week functional electrical stimulation did not significantly change cardiac function or structure; there was no significant difference in changes of E/A, E/e’ or left atrial volume between the stimulation and control groups.39 Despite the neutral effect on cardiac structure or function, functional electrical stimulation improved 6MWD (52.8 m; p<0.01) compared with control group.
Similar results were reported in the TRAINING-HF trial.36 Specifically, 12-week functional electrical stimulation did not significantly change cardiac function or structure; there was no significant difference in changes of E/e’ or left atrial volume index between the stimulation and control groups. Despite the neutral effect on cardiac structure or function, functional electrical stimulation improved peak VO2 (2.93 ml/min/kg; p<0.001) compared with the control group.
The possible mechanisms underlying the improved exercise capacity with the functional electrical stimulation in HFpEF patients include the improvement of endothelial function.39 In HFpEF patients, endothelial function is impaired and is an important contributor to exercise intolerance.29
Perspectives
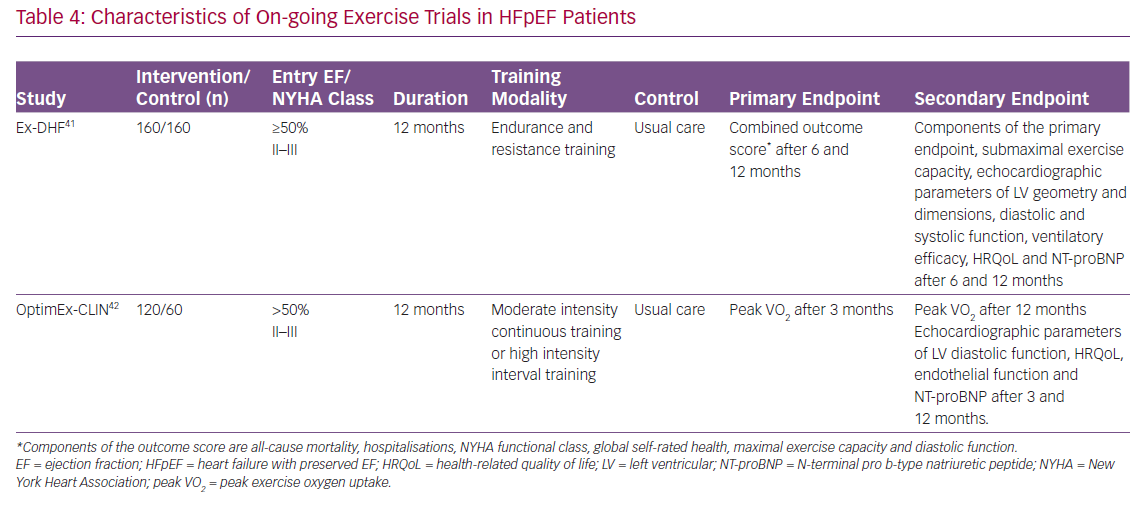
As described above, recent RCTs and meta-analyses of RCTs have shown that physical training such as cycling or walking, inspiratory muscle training and functional electrical stimulation can improve exercise capacity in HFpEF patients. Nevertheless, clinicians should take several points into consideration. First, although not specific to this topic, RCTs usually have strict enrolment criteria, and thus, the findings of the RCTs cannot be generalised to routine clinical practice. Specifically, in most of the trials listed in Tables 1–3, patients with cardiac and non-cardiac comorbidities such as AF, coronary artery disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, chronic kidney disease and anaemia were excluded. Importantly, registry studies have reported that HFpEF patients commonly have these co-morbidities.40 Thus, the reported beneficial effect of physical training may not be extended into real-world HFpEF patients. Further studies are warranted to examine the effect of physical training on functional capacity in HFpEF patients with these co-morbidities. Second, the most effective type, intensity, frequency and duration of training are not determined in HFpEF patients. There are several on-going exercise trials in HFpEF patients that are expected to be published (Table 4). Specifically, the Exercise Training In Diastolic Heart Failure (Ex-DHF) trial is designed to investigate whether long-term (12-month) supervised exercise training can improve a clinically meaningful composite outcome score in HFpEF patients.41 Components of the outcome score are all-cause mortality, hospitalisations, New York Heart Association functional class, global self-rated health, maximal exercise capacity and diastolic function after 6 and 12 months. The Optimizing Exercise Training In Prevention and Treatment of Diastolic Heart Failure (OptimEx-CLIN) trial aims to define the optimal dose of exercise training in patients with HFpEF.42 Patients with stable symptomatic HFpEF will be randomised (1:1:1) to moderate intensity continuous training, high intensity interval training or a control group. The primary endpoint of the OptimEx-CLIN trial is peak VO2 after 3 months. The results of these trials may provide further insights into exercise prescriptions in HFpEF patients.
Conclusion
In summary, available evidence suggests that physical training in addition to standard HF medication can provide clinically relevant improvements in exercise capacity without significant changes in LV function or structure in HFpEF patients. Further studies are necessary both to elucidate more exact mechanisms of exercise intolerance and to develop recommendations regarding the most effective training approach, including type, intensity, frequency and duration, in patients with HFpEF.